Attenuation signal reduction to dB: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Many fiber optic technicians are unfamiliar with logarithmic scales and units such as decibel (dB). | Many fiber optic technicians are unfamiliar with logarithmic scales and units such as decibel (dB). | ||
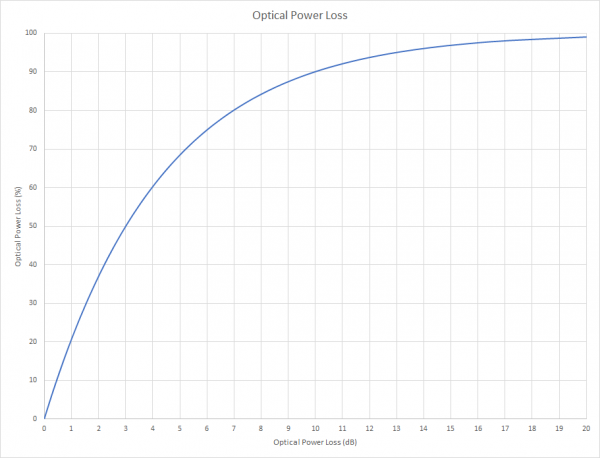
This table allows you to get a grasp on the relationship between optical power loss on a | This table allows you to get a grasp on the relationship between optical power loss on a logarithmic scale (dB) and optical power loss on a linear scale (%). | ||
Power Loss as | Power Loss (dB) is also known as Attenuation (dB). | ||
| | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
Optical Power Loss (%) | Optical Power Loss (%) | ||
| |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| style="text-align: center" | 96.8% | | style="text-align: center" | 96.8% | ||
|} | |} | ||
| |||
| | ||
Latest revision as of 14:59, 4 May 2024
Introduction
Many fiber optic technicians are unfamiliar with logarithmic scales and units such as decibel (dB).
This table allows you to get a grasp on the relationship between optical power loss on a logarithmic scale (dB) and optical power loss on a linear scale (%).
Power Loss (dB) is also known as Attenuation (dB).
Solution
Table
|
Optical Power Loss (dB) Attenuation (dB) |
Optical Power Loss (%)
|
|---|---|
| 0 dB | 0% |
| 1 dB | 21% |
| 2 dB | 37% |
| 3 dB | 50% |
| 4 dB | 60% |
| 5 dB | 68% |
| 6 dB | 75% |
| 7 dB | 80% |
| 10 dB | 90% |
| 13 dB | 95% |
| 15 dB | 96.8% |
Graph